
Language Morphology – The study of the rules governing how morphemes, the minimal meaningful units of language, are used in a language. Phonology is the study of the speech sound (phoneme) system in a language, including the rules for combining and using phonemes. Morphological processes must combine individual morphemes’ phonological content in order to produce a phonological representation that can be driven by phonological processes. In spoken communication, both morphological and phonological processes are highly connected. These two subjects are necessary for language analysis. The language in which a word is used is referred to as a morpheme. Language phonology is the study of the sounds and sounds systems of the language. Our spoken language consists of the expression “pronunciation.” The sounds in a language are referred to as phonology.
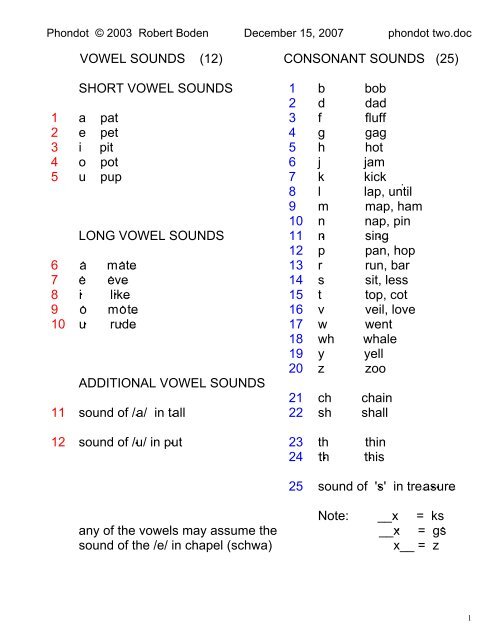
The phonology of pronunciation is in action. Consonants are classified according to their place of articulation, manner of articulation, and phonation. The airstream that flows through the vocal tract during speech is known as the phonatory airstream. The production of consonants requires the use of the breath, which is controlled by the lungs.
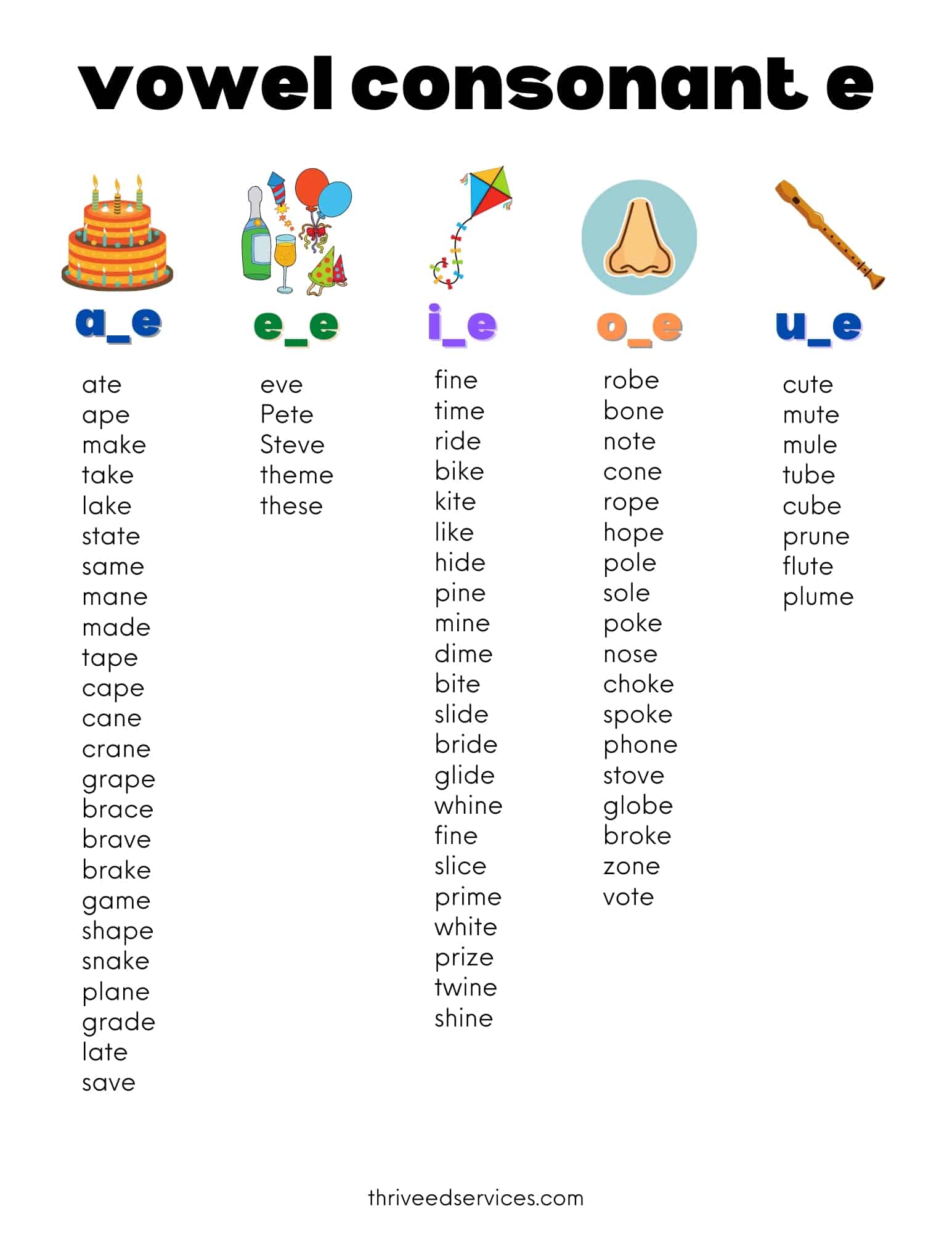
Consonants are produced when the vocal cords vibrate during speech. In phonology, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
